Missed a GST due date and now worried about penalties or interest? You are not alone. Many business owners in India face GST penalties because of late return filing, late tax payment, or simple compliance mistakes. The problem is not just the penalty amount-it is the confusion around how much you need to pay, how it is calculated, and whether anything can be waived.
This guide explains everything you need to know about GST penalties in India in clear and simple language. You will understand the different types of GST penalties, the late payment penalty and interest, how GST penalties are calculated, how to pay them correctly on the GST portal, and when you may be eligible for a GST penalty or interest waiver under government schemes. No complicated legal words-just practical explanations with real-life clarity.
This article is written for small business owners, traders, freelancers, startups, and anyone responsible for GST compliance. Whether you have already received a notice or want to stay safe in the future, this GST penalty guide will help you make informed decisions and avoid unnecessary costs.
Disclaimer: This article is for information purposes only. GST laws and penalties may change. Always consult a qualified tax professional for advice specific to your case.
What Is a GST Penalty and Why Does It Matter?
A GST penalty is an extra amount that the government charges when a taxpayer does not follow GST rules on time or correctly. In simple words, it is a cost you pay for GST non-compliance. This can happen if you file your GST returns late, pay tax after the due date, report incorrect figures, issue wrong invoices, or fail to register under GST when required.
Many people think GST penalties apply only in serious cases, but that is not true. Even a small delay or mistake can lead to additional costs. That is why understanding the meaning of GST penalty is important for every business, big or small.
Difference Between GST Late Fee, Interest, and Other Penalties
GST law has different types of charges, and each one applies in a different situation. Knowing the difference helps you understand what you actually owe.
Late Fee (for late return filing)
A late fee is a fixed amount charged per day when you submit a GST return after the due date. It works like a fine for not filing your return on time. The amount depends on whether your return has a tax liability or is a nil return, and it is automatically calculated by the GST portal when you file late. Late fees are mainly applied under Section 47 of the CGST Act.
Interest (for late tax payment)
Interest is charged when you pay GST after the due date, even if you filed the return. Unlike late fees, interest is calculated as a percentage per year on the unpaid tax amount. You can think of interest as “rent” you pay for using government money beyond the allowed time. Interest is covered under Section 50 of the CGST Act and continues to increase for every day of delay.
Other GST Penalties
Apart from late fees and interest, the GST law also includes penalties for serious or repeated non-compliance. These may apply if you do not register under GST when required, issue incorrect or fake invoices, claim input tax credit wrongly, or intentionally hide taxable turnover. In such cases, the penalty can be much higher than regular late fees and may even involve legal action in extreme situations.
Understanding the difference between GST interest and penalty helps you avoid surprises when checking your liability on the GST portal.
Why Ignoring GST Penalties Can Be Risky
Ignoring GST penalties does not make them go away. If penalties and interest remain unpaid, they keep adding up over time and can put pressure on your cash flow. The GST department may send notices demanding payment, block your ability to file future returns, or delay and withhold GST refunds.
In serious cases, especially where fraud or intentional tax evasion is involved, GST penalties can lead to prosecution and heavy financial consequences. That is why timely action is important. By understanding GST penalties under the CGST Act and responding early, you can reduce financial damage and stay compliant without stress.
Knowing how GST penalties work is the first step toward protecting your business from unnecessary losses.
Types of GST Penalties You Should Know
GST penalties are not the same in every situation. The law applies different charges depending on what went wrong-late filing, late payment, or serious non-compliance. Understanding these categories helps you quickly identify your risk and estimate the extra cost.
Below are the most common types of GST penalties that taxpayers face in India.
Late Filing of GST Returns (GSTR-3B, GSTR-1, etc.)
Late filing is the most common reason businesses pay GST penalties. If you submit your GST return after the due date, the GST portal automatically applies a late fee per day until you file the return.
- For normal (non-nil) returns:
The late fee is ₹50 per day-₹25 under CGST, and ₹25 under SGST. - For nil returns (no tax liability):
The late fee is reduced to ₹20 per day-₹10 CGST, and ₹10 SGST.
This late fee starts counting from the day after the due date and continues until the return is filed. The GST system calculates it automatically, so you cannot edit or reduce it manually while filing.
There is also a maximum cap on late fees per return. In many commonly applied notifications, this cap is ₹5,000 per return (combined CGST and SGST). However, GST rules and relaxations change from time to time, so it is always important to check the latest notifications before assuming the final amount.
A common question is about IGST. For delayed returns, there is no separate IGST late fee. The late fee is charged only under CGST and SGST, even if your transaction falls under IGST.
This means even a short delay can add up if multiple months are pending. That is why people often search for answers to questions like how much penalty for late GST filing or GSTR-3B late fee per day.
Late Payment of GST (Tax Paid After Due Date)
Late payment of GST attracts interest, not a fixed late fee. Interest applies when you file the return but pay the tax after the due date, or when tax liability remains unpaid for any reason.
- Standard interest rate:
GST interest is charged at 18% per year on the delayed tax amount. - Higher interest rate (24% per year):
This applies in cases where excess input tax credit (ITC) is wrongly claimed, or output tax liability is reduced incorrectly.
Interest is calculated daily and applies from the day after the due date until the actual date of payment. In most cases, interest is calculated on the gross tax liability for the delayed period, not just the net amount you plan to pay later.
Many taxpayers are surprised because interest keeps increasing silently until payment is made. This is why GST late payment penalty and interest can become costly if ignored for several months.
Penalties for Non-Compliance (Registration, Invoice, Evasion)
Apart from late filing and late payment, the GST law also imposes penalties for more serious compliance failures. These penalties are usually higher and apply when rules are violated beyond simple delays.
- No GST registration or late registration:
If you were required to register under GST but did not, the penalty can be equal to the tax amount involved or a minimum of ₹10,000, whichever is higher. - Incorrect invoices or wrong details:
Issuing incorrect tax invoices, showing wrong GSTIN, or misleading details can attract a fixed penalty, commonly up to ₹25,000, depending on the nature of the error. - Tax evasion or wilful misstatement:
Intentional suppression of sales, fake invoicing, or misuse of input tax credit can result in heavy penalties and, in extreme cases, prosecution. These cases are treated much more seriously than regular late filings.
These penalties are meant to discourage misuse of GST and protect honest taxpayers. Understanding penalties for not registering under GST, incorrect GST invoices, and tax evasion can help businesses stay on the safe side of the law.
How to Calculate GST Late Fees and Interest (Step-by-Step)
Many taxpayers panic when they see a higher-than-expected amount on the GST portal. In most cases, the extra amount is simply late fees or interest. This section explains how to calculate GST penalty step by step, so you clearly understand where the numbers come from before making a payment.
Step 1 – Identify What Went Wrong
Before calculating anything, you must first identify the type of delay or mistake. Ask yourself these simple questions:
- Was the GST return filed late?
If yes, late fees will apply. - Was the tax paid after the due date?
If yes, interest will apply. - Did both happen?
In many cases, both late fees and interest are charged together.
Next, identify:
- Which return is delayed?
For example, GSTR-3B, GSTR-1, or any other applicable return. - Which tax period is involved?
Month and financial year matter for accurate calculation. - Is it a nil return or a return with tax liability?
This affects the daily late fee amount.
Once this is clear, calculating the exact GST penalty becomes easy.
Step 2 – Calculate Late Fee for Late Filing
Late fees apply only when a return is filed after the due date, regardless of whether tax is payable or not.
Simple formula:
Late fee = Per-day late fee × Number of days delayed
(This is subject to a maximum cap per return.)
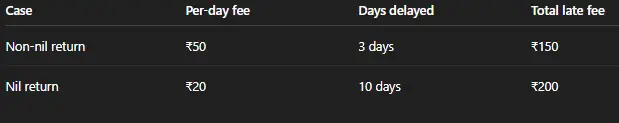
Per-day late fee rates:
- Non-nil return: ₹50 per day (₹25 CGST + ₹25 SGST)
- Nil return: ₹20 per day (₹10 CGST + ₹10 SGST)
The late fee is capped per return (commonly up to ₹5,000), but this cap may change based on government notifications, so it is always advisable to verify the latest rule.
Examples:
- Example 1: Non-nil return
Delay: 3 days
Late fee: 3 × ₹50 = ₹150 total
(₹75 CGST + ₹75 SGST) - Example 2: Nil return
Delay: 10 days
Late fee: 10 × ₹20 = ₹200 total
Illustration table:
Step 3 – Calculate Interest on Late Payment
Interest applies when GST tax is paid after the due date, even if the return is filed.
Interest formula:
Interest = Outstanding tax × (Interest rate per year ÷ 365) × Number of days delayed
- Standard interest rate: 18% per year
- Calculated from the day after the due date until the actual payment date.
Example 1:
GST tax payable: ₹50,000
Delay: 20 days
Interest = 50,000 × (18% ÷ 365) × 20
Interest ≈ ₹492
Example 2 (simple round numbers):
GST tax payable: ₹1,00,000
Delay: 10 days
Interest ≈ ₹493
Interest keeps increasing every day until payment is made, which is why timely payment is important even if return filing is slightly delayed.
Step 4 – Combine Late Fee + Interest + Tax
The final amount payable in GST is the total of:
Tax payable + Late fee + Interest
This combined liability is what you see in the payment and liability section of the GST portal before filing the return or creating a challan. You must clear the full amount to successfully file the return and remain compliant.
Understanding this process removes confusion and helps you avoid overpaying or delaying payments further. With the right calculation, you can confidently handle GST penalties without stress.
This step-by-step method answers common queries like how to calculate GST penalty, GST late fee calculator, and GST interest calculation examples, making GST compliance easier to manage.
How to Pay GST Penalty and Interest on the GST Portal
Once you know the exact late fee or interest payable, the next step is making the payment correctly on the GST portal. The good news is that GST penalties and interest are paid online, and in most cases, the system calculates the amount automatically.
Below are the two common and practical ways to pay GST penalty and interest, depending on your situation.
Method 1 – While Filing a Delayed Return (GSTR-3B / GSTR-1)
This is the most common method used when your GST return is filed after the due date.
Step-by-step process:
- Log in to the GST portal using your GSTIN, username, and password.
- Go to Services → Returns → Returns Dashboard.
- Select the Financial Year and Return Filing Period.
- Click on the relevant return, such as GSTR-3B or GSTR-1.
- Start filing the return.
The system will automatically calculate late fees and interest based on the delay.
Tax payable
Late fee (if return filed late)
Interest (if tax paid late)
6. Check the “Liability” or “Payment” section to view:
- Tax payable
- Late fee (if return filed late)
- Interest (if tax paid late)
7. If your cash ledger has a sufficient balance, use it to pay.
8. If the balance is insufficient:
- Click Create Challan
- Make payment using net banking, NEFT/RTGS, or other available modes.
9. Once payment is completed, submit and file the return.
You cannot manually change or avoid the late fee and interest at this stage. The GST portal calculates it automatically as per the law.
Before filing, many taxpayers use GST calculators available on platforms like ClearTax or GST software tools to estimate late fees and interest, so there are no surprises at the time of payment.
Method 2 – Paying Additional Penalty or Interest via Challan / DRC
This method is used when:
- You receive a GST demand order (such as DRC-07), or
- You realise later that an additional interest or penalty is payable voluntarily.
Steps to pay using a challan (GST PMT-06):
- Log in to the GST portal.
- Go to Services → Payments → Create Challan.
- Select Form GST PMT-06.
- Enter the payable amount under the correct minor head, such as:
- Interest
- Penalty
- Tax (if applicable)
5. Choose the payment mode:
- Net banking
- NEFT / RTGS
- Over-the-counter (if applicable)
6. Complete the payment and generate the challan.
7. After payment, the amount will reflect in your cash ledger and can be adjusted against the liability.
Important:
Always download and save the challan and payment receipt. These documents are useful for future reference, audits, appeals, or resolving mismatches with the GST department.
Understanding the GST penalty payment process helps you clear dues smoothly without errors or delays. Whether you are paying late fees while filing a delayed return or settling interest through a challan, following the correct steps ensures your GST compliance remains intact.
This section answers common queries such as how to pay the GST late fee, how to pay GST penalty online, and how GST interest payments work on the portal.
GST Penalty Waiver and Amnesty Schemes (Section 128 & 128A)
GST law understands that genuine taxpayers may sometimes fail to comply due to confusion, lack of awareness, or financial stress-especially during the early years of GST. That is why the government has provided waiver and amnesty provisions to reduce or completely remove penalties and interest in specific cases.
This section is important because it explains when you can legally reduce or avoid GST penalties, instead of paying the full amount blindly.
Regular Waiver Power under Section 128
Under Section 128 of the CGST Act, the government has the power to reduce or waive late fees for GST returns for specific tax periods through official notifications.
In simple terms, this means:
- The government can announce amnesty or relief schemes.
- These schemes usually apply to late filers who have not submitted GSTR-3B, GSTR-1, or other returns for past months or years.
- In many past schemes, late fees were reduced to a very small amount or completely waived, provided the taxpayer filed the pending returns within a given time window.
Such waivers are not automatic. They apply only:
- For specific periods mentioned in the notification, and
- If returns are filed within the deadline announced under the scheme.
This is why staying updated with GST notifications is critical.
New Amnesty Scheme under Section 128A (2024–25)
Section 128A is a major relief measure and one of the most important recent updates in the GST law. It focuses not only on late fees, but also on interest and penalties related to GST demand cases.
What Section 128A Allows (in Simple Words)
Section 128A allows waiver of interest, penalty, or both for certain GST demand cases, provided the taxpayer pays the full tax amount within the specified time.
This scheme mainly applies to:
- GST demands raised under Section 73 (cases involving non-fraud, such as mistakes or genuine errors).
- Financial Years 2017–18, 2018–19, and 2019–20.
If you fall under this category and clear the tax due on time, the interest and penalty portion can be completely waived, as per the scheme conditions.
Key Conditions You Must Know
- The GST notice or order must be issued under Section 73, not fraud-related sections.
- The taxpayer must pay the full tax amount demanded for the eligible financial years.
- The waiver becomes invalid if the remaining payable tax is not paid within the specified time limit (commonly mentioned as three months from the date of the order, as per circulars).
- If an appeal is already filed, it must be withdrawn to avail the benefit.
- Proof of withdrawal (such as a screenshot or acknowledgement) must usually be uploaded as per GSTN advisory instructions.
This scheme is especially useful for taxpayers who were stuck in long-pending GST disputes and want a clean closure.
Important Note on Timelines
The GST amnesty scheme under Section 128A is time-bound. The dates, forms, and conditions are announced through official notifications and advisories. Taxpayers should always check the latest updates on the GST portal or consult a GST professional before applying.
How to Apply for a Waiver on the GST Portal (SPL-02 and Related Forms)
Applying for a waiver is done online through the GST portal. The process is straightforward but must be done carefully.
High-level application process:
- Log in to the GST portal using your credentials.
- Go to Services → My Applications.
- Select “Apply for Waiver Scheme under Section 128A” or the relevant option shown on the portal.
- Fill in the required details in Form SPL-02.
- Upload supporting documents, such as:
- Proof of tax payment
- Withdrawal of appeal (if applicable)
7. The GST department reviews the request and issues an order (such as SPL-05 or SPL-06).
8. If any balance amount is mentioned, pay it within the prescribed deadline to keep the waiver valid.
Why This Section Matters for Taxpayers
Many taxpayers unnecessarily pay full interest and penalty simply because they are not aware of the waiver schemes. Understanding GST penalty waiver rules, especially under Section 128A, can save a significant amount of money and bring long-pending GST matters to a close legally and peacefully.
This section directly addresses common searches like GST penalty waiver, GST amnesty scheme 2024, and Section 128A waiver of interest or penalty, making it one of the most valuable parts of this guide.
How to Avoid GST Penalties in the Future (Practical Checklist)
GST penalties are avoidable in most cases. The key is not complex knowledge, but discipline, planning, and timely action. If you follow a simple system, you can protect your business from late fees, interest, and unnecessary stress.
Below is a practical checklist that helps you stay compliant and avoid GST penalties in the long run.
Maintain a Proper GST Due-Date Calendar
The most effective way to avoid GST late fees is to never miss a due date.
Create and maintain a GST calendar that clearly mentions:
- GSTR-1 due dates
- GSTR-3B due dates
- Annual return (GSTR-9 / 9C, if applicable)
- Any other periodic GST filings relevant to your business
Mark these dates at the start of the financial year, not month by month. This habit alone can help you avoid most GST penalties.
Use Auto-Reminders and Alerts
Do not rely on memory or last-minute panic.
Set up automatic reminders using:
- Google Calendar alerts
- WhatsApp reminder groups
- Accounting or practice management tools
Ideally, set two reminders:
- One reminder 7 days before the due date
- One reminder 2 days before the due date
This gives you enough buffer time to arrange data or funds if needed.
Reconcile Books with GSTR-2B Regularly
Mismatch between your books and GSTR-2B is a major reason for GST notices and penalties.
Make it a routine to:
- Reconcile purchase data with GSTR-2B every month
- Identify missing or mismatched invoices early
- Follow up with vendors for corrected invoices before filing returns
Regular reconciliation reduces the risk of wrong ITC claims, which can trigger interest, penalties, or demand notices later.
Pay Estimated Tax on Time (Even If Books Are Not Final)
If your books are not fully closed before the due date, do not delay payment.
A smart approach is to:
- Pay the estimated GST liability on time
- Adjust minor differences in the next return
Paying GST late attracts interest, even if the return filing is done later. Paying on time protects your cash flow from unnecessary interest costs.
Paying GST late attracts interest, even if the return filing is done later. Paying on time protects your cash flow from unnecessary interest costs.
Check GST Portal Notices and Emails Regularly
Many taxpayers miss penalties simply because they ignore the GST portal communication.
Make it a habit to:
- Log in to the GST portal regularly
- Check notices, alerts, and messages
- Read emails and SMS from the GST department seriously
Early response to a notice can often prevent escalation into penalties, demand orders, or blocked filings.
Consult a GST Expert Instead of Guessing
GST law changes frequently. Guessing or relying on outdated information can be expensive.
Consult a GST professional when:
- You are unsure about the tax calculation or ITC
- You receive a notice or a demand order
- You plan to regularise past non-compliance
- You want to check eligibility for waiver or amnesty schemes
Professional advice may seem like an extra cost, but it often saves far more money by avoiding penalties and interest.
Final Thought
Avoiding GST penalties is not about doing everything perfectly-it’s about doing things on time and fixing issues early. With a simple checklist, basic reminders, and expert support when needed, you can stay GST-compliant without stress.
This section answers common user queries, such as how to avoid GST penalty, avoid GST late fee, and tips to stay GST compliant, while building long-term trust with your audience.
When You Should Talk to a GST Professional (and How an Accure Tax Consultant Can Help)
Many GST issues look small at first, but can become expensive if not handled correctly. While routine filing may be manageable, certain situations clearly require professional guidance. Knowing when to take expert help can save you money, time, and legal trouble.
Situations Where Professional GST Help Is Critical
You should strongly consider speaking to a GST consultant if any of the following apply to you:
- You have multiple pending GST returns
When several months or years of returns are pending, calculating the exact late fee and interest manually becomes confusing. A professional can assess the full impact and suggest the most cost-effective way to close all pending periods. - You have received a show cause notice or penalty order
GST notices are legal documents. A wrong reply—or no reply at all—can lead to higher penalties, demand orders, or blocked filings. Expert review helps you understand what the department is asking and how to respond correctly and on time. - You want to apply for an amnesty or penalty waiver
Schemes under Section 128 or 128A have conditions, timelines, and documentation requirements. A GST professional can quickly check eligibility, guide you on appeal withdrawal (if required), and help you avoid mistakes that may invalidate the waiver. - You want to regularise past non-compliance without overpaying
Businesses that ignored GST for some time often pay more than required out of fear. A professional review ensures you pay only what is legally required, not unnecessary penalties.
In short, if your GST issue involves older periods, notices, or high amounts, expert assistance is not optional-it is essential.
How Accure Tax Consultant Can Help You
At Accure Tax Consultant, the focus is not just on compliance, but on practical, cost-saving solutions tailored to your business.
Here’s how professional support can make a real difference:
- Accurate calculation of GST interest and penalties
We calculate exact late fees and interest for all pending periods, so you know the real exposure before making any payment. - Support for GST penalty waivers and amnesty schemes
From checking eligibility under Section 128A to filing waiver applications, withdrawing appeals, and tracking deadlines—we handle the complete process. - Replies to GST notices and appeal support
Drafting clear, legally correct replies to show cause notices and penalty orders helps avoid escalation and unnecessary litigation. - Setting up a simple compliance system
We help you put a basic GST compliance framework in place—reminders, reconciliations, and filings—so penalties do not repeat in the future.
Why Expert Guidance Matters
GST law is technical and constantly evolving. Professional help is not just about avoiding mistakes—it is about making informed decisions with confidence.
If you’re facing uncertainty around GST penalties, working with a reliable GST penalty consultant ensures clarity, savings, and long-term peace of mind.
With the right guidance, GST compliance becomes manageable—not stressful.
Conclusion – Clear Your Past, Protect Your Future
GST penalties do not have to feel overwhelming. When you understand the rules, calculate late fees and interest correctly, pay only what is required, and use waiver or amnesty schemes where available, GST compliance becomes manageable. The real key is acting early and setting up a simple system so the same mistakes do not repeat.
If you are unsure where to begin or worried about past delays, Accure Tax Consultant can help. Our team can review your complete GST history, calculate exact penalties and interest, guide you through waiver or amnesty schemes, and set up a compliance process that protects your business in the future.
Clear your past GST issues with confidence, you can focus on growing your business without fear of penalties.
FAQs on GST Penalty, Interest, and Waiver
These frequently asked questions are based on what taxpayers commonly search on Google and what clients usually ask in real-life GST cases. The answers are kept short, clear, and practical, with no legal jargon.
1. How much is the penalty for the late filing of GSTR-3B?
The late fee for GSTR-3B is ₹50 per day (₹25 CGST + ₹25 SGST) if there is tax liability. For nil returns, it is ₹20 per day. The total late fee is subject to a maximum cap per return, as notified by the government.
2. Is the GST late fee calculated per day or per month?
GST late fee is calculated per day, not per month. It starts from the day after the due date and continues until the return is filed on the GST portal.
3. How are GST penalties calculated?
GST penalties depend on the type of non-compliance. Late filing attracts a fixed late fee per day, while late payment of tax attracts interest (usually 18% per year) calculated daily. Other penalties depend on specific violations.
4. Can I claim the GST penalty as a business expense?
No, GST penalties and late fees are not allowed as business expenses under income tax laws. Interest paid on delayed tax may be allowed in limited cases, but penalties are generally not deductible.
5. Is there any penalty for late GST registration?
Yes. If you were required to take GST registration and failed to do so, the penalty can be ₹10,000 or the tax amount involved, whichever is higher. Additional interest may also apply to unpaid tax.
6. What if I can’t pay the GST penalty immediately?
If payment is delayed, interest will continue to increase on the unpaid amount. In some cases, you may pay the tax first and then explore waiver or relief schemes for interest and penalty, or seek professional advice for the best approach.
7. Can I get a refund of the penalty already paid if there is a new waiver?
In most cases, penalties already paid are not refunded, even if a new waiver or amnesty scheme is introduced later. Waivers usually apply to unpaid or pending liabilities only.
8. Can the GST penalty be waived completely under the new amnesty scheme?
Yes, under the GST amnesty scheme (Section 128A), interest and penalties may be completely waived for eligible cases if the full tax amount is paid within the specified time and all conditions are met.
9. How to waive the GST penalty?
GST penalty can be waived only if a government notification or amnesty scheme allows it. You must meet the eligibility conditions and apply through the GST portal using the prescribed form within the deadline.
10. How to apply for a waiver of interest and penalties?
You need to log in to the GST portal, go to My Applications, select the waiver scheme (such as under Section 128A), fill in the application form, upload the required documents, and submit it for approval.
11. What happens if I do not respond to a GST penalty notice?
Ignoring a GST penalty notice can lead to higher demand orders, blocked return filing, recovery action, or legal proceedings. Always respond within the deadline or consult a GST professional immediately.